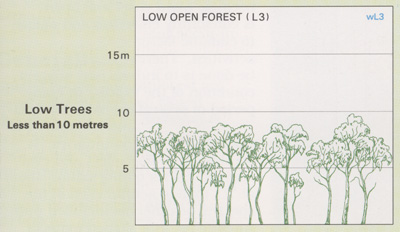
Eucalypt Low Open Forests
- Contain trees with heights from 5m to 10m.
- Grow on less favourable sites (e.g. under
extreme cold or dry conditions; poor soil
nutrients; waterlogging; and steep rocky slopes).
- Eucalypt species may be the same as those
occurring in nearby more favourable sites that
support Eucalypt Open Forests. Within some
stands of this vegetation, there may be a graduated
change in dominant species with change
in growing constraints (e.g. the snow gum,
Eucalyptus pauciflora replaces other eucalypts
as elevation increases in subalpine areas).
- Exhibit a variety of subforms, with understoreys ranging from low trees and shrubs to tussock grasses or, in some cases, bare ground.
Some areas of this vegetation have been cleared. Many of the remaining areas, although small, may be relatively intact as the extremes in site conditions make them of limited value for pastoral or agricultural use.
![]() Photos from the Australian Plant Image Index
Photos from the Australian Plant Image Index
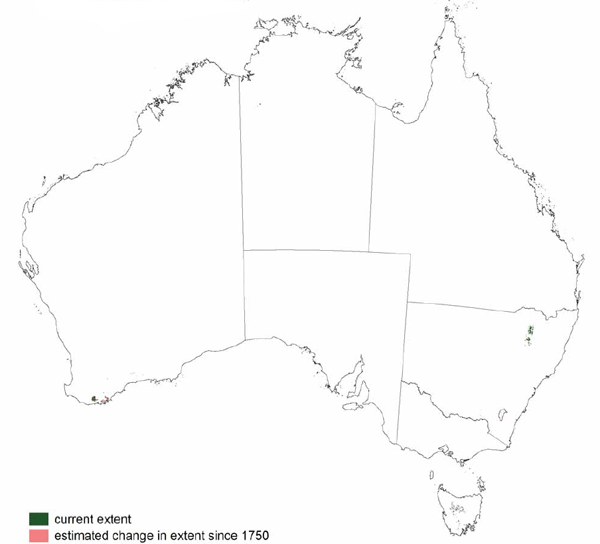
Sources: Australia's Native Vegetation - from rainforest to spinifex, map and information poster produced by the National Land & Water Audit, Natural Heritage Trust, Australian Government, 2001
Australia's Native Vegetation - A summary of Australia's Major Vegetation Groups, 2007, Australian Government website
https://www.environment.gov.au/system/files/resources/a9897cf2-9d38-4201-bea2-13dadf3af9a8/files/major-veg-summary.pdf
Structure diagram: Atlas of Australian Resources - Vol. 6, Vegetation,
AUSLIG, Canberra, 1990
![An Australian Government Initiative [logo]](/images/austgovt_brown_90px.gif)